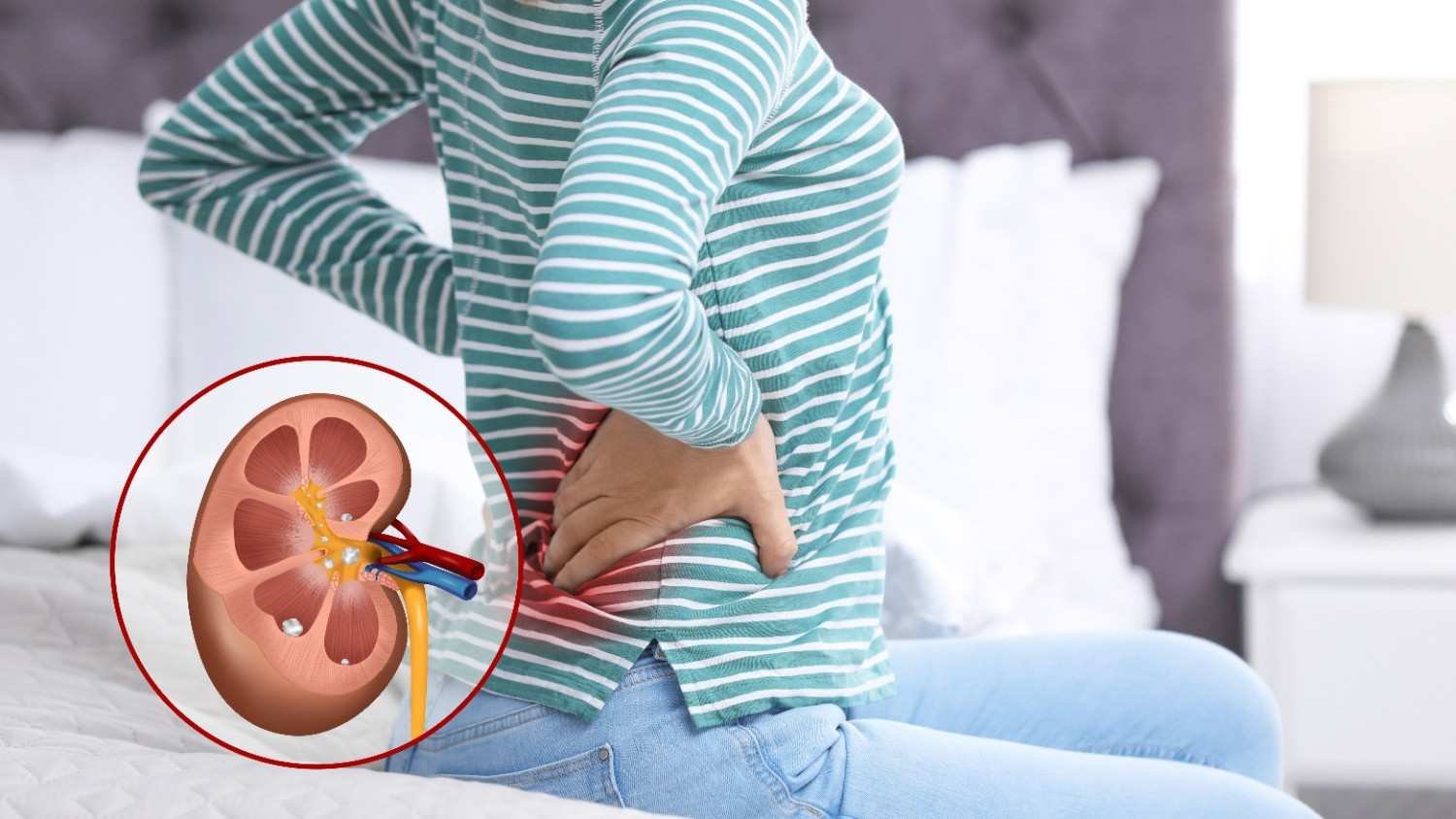
Kidney stones have been a source of discomfort for humans for centuries. These tiny, solid deposits form in the kidneys due to the buildup of minerals and salts. Essentially, they’re like small pebbles that can cause significant pain and complications.
Fast-forward to modern times, and while we now have advanced healthcare solutions, kidney stones still manage to take us by surprise. Recognizing the early symptoms of kidney stones can make all the difference in addressing them before they escalate.
Let’s dive into your body’s subtle hints—the early symptoms of kidney stones that you should never ignore. Stay informed and proactive to safeguard your health! If you are facing severe Kidney Transplants, then you should consult Dr. Nisha Gaur. Dr. Nisha Gaur is the most reputed Nephrologist doctor in Jaipur and has years of work experience and is the Best Nephrologist in Jaipur for Chronic Kidney Disease Care and also for treating ailments such as Kidney Transplantation, Peritoneal Dialysis, Hemodialysis, and Kidney Biopsy.
Kidney Stone
Kidney stones, also known as renal calculi, are solid mineral and salt deposits in the kidneys or urinary tract. These stones can vary in size, shape, and composition, ranging from tiny crystals to larger stones that can cause excruciating pain and complications.
Kidney stones develop when certain substances in the urine, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid, become highly concentrated and crystallize.
Early Warning Signs of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can occur at any age and they can have various symptoms. Here are some of the early signs of kidney stone
- Severe Pain: One of the most unmistakable early symptoms of kidney stones is intense pain, often described as sharp and stabbing. This pain usually occurs in the back, side, abdomen, or groin and can radiate to other areas. It tends to come in waves, lasting from minutes to hours and is often accompanied by sweating and restlessness.
- Urinary Changes: Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, is a hallmark sign of kidney stones. The urine may appear pink, red, or brownish due to irritation caused by the stone’s movement through the urinary tract—an early symptom that should not be overlooked.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, is a hallmark sign of kidney stones. The urine may appear pink, red, or brownish due to irritation caused by the stone’s movement through the urinary tract—an early symptom that should not be overlooked.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many people with kidney stones experience nausea and vomiting, especially when the stones create blockages or trigger severe pain. These early symptoms of kidney stones can be quite debilitating and often necessitate medical intervention.
- Fever and Chills: In some instances, kidney stones can lead to urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney infections (pyelonephritis), which manifest as fever, chills, and general malaise. These symptoms signal a more serious complication requiring immediate medical attention.
Variation in Symptoms:
Understanding the variation in symptoms of kidney stones is essential, as it underscores the complexity of this condition and the diverse ways it can manifest in different individuals. Recognizing the early symptoms of kidney stones is crucial because, while some people may experience classic signs like severe pain and blood in the urine, others might present with more subtle or atypical symptoms. Here’s a more detailed exploration of the variation in symptoms:
- Intensity of Pain: The severity of pain associated with kidney stones can vary significantly among individuals. While some may experience excruciating, debilitating pain requiring immediate medical attention, others may endure milder discomfort. Recognizing this variation is important when identifying the early symptoms of kidney stones, as factors such as stone size, location, and individual pain thresholds play a critical role.
- Location of Pain: The specific location of pain caused by kidney stones often depends on the stone’s position within the urinary tract. For instance, stones in the kidneys may result in flank pain, while those in the ureter could cause lower abdominal or groin pain. Understanding these nuances helps pinpoint the early symptoms of kidney stones and guides diagnostic evaluation.
- Duration of Symptoms: The duration of symptoms related to kidney stones can range from intermittent episodes over days or weeks to persistent and severe symptoms. This variability highlights the importance of recognizing the early symptoms of kidney stones early on to prevent complications and seek timely treatment.
- Presence of Associated Symptoms: Beyond pain and urinary changes, kidney stones may present with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and general malaise. These associated symptoms, often considered among the early symptoms of kidney stones, can offer insights into potential complications such as urinary tract infections or kidney damage.
- Individual Factors: Factors such as age, gender, overall health, and underlying medical conditions influence how kidney stones manifest. Older adults, for example, may exhibit atypical symptoms or be more prone to complications. These individual differences underscore the diverse presentations of kidney stones and the importance of being vigilant about their early signs.
Treatment Options for Kidney Stones:
The treatment approach for kidney stones depends on various factors, including the size, location, and composition of the stone, as well as the severity of symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Drink Plenty of Water: Adequate fluid intake is crucial for preventing kidney stones and promoting their natural passage. Drinking plenty of water helps dilute urine and flush out minerals that contribute to stone formation.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate the pain associated with kidney stones. Your healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications if necessary.
- Medical Therapy: Depending on the size and composition of the stone, medications such as alpha-blockers or calcium channel blockers may be prescribed to help relax the muscles of the urinary tract and facilitate stone expulsion.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL): ESWL is a non-invasive procedure that uses shock waves to break up kidney stones into smaller fragments, making them easier to pass through the urinary tract.
- Ureteroscopy and Laser Lithotripsy: For larger or more stubborn stones, ureteroscopy may be performed, where a thin scope is inserted into the urethra and bladder to locate and remove the stone using laser energy.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases where other treatments are ineffective or the stone is too large to pass naturally, surgical removal may be necessary. This may involve traditional open surgery or minimally invasive techniques such as percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PNL).
Conclusion:
Kidney stones are a common and often painful condition that requires prompt diagnosis and appropriate management. By understanding the formation, symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies for kidney stones, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and maintain kidney health. Recognizing the early symptoms of kidney stones is key to preventing further complications. If you are facing severe kidney issues or suspect the presence of kidney stones, you should consult Dr. Nisha Gaur. With over a decade of experience as the Best Nephrologist in Jaipur, she is the best Nephrologist in Jaipur for chronic kidney disease care, kidney transplants, peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, and kidney biopsy.