Creatinine is one of the most important markers of kidney health. When your creatinine level rises, it may indicate that your kidneys are not filtering waste properly. In 2025, doctors increasingly rely on creatinine + eGFR to detect kidney disease early.
This guide explains:
- Updated Creatinine levels chart
- Normal vs high creatinine
- Early symptoms of high creatinine
- The real causes
- 7 fast and effective ways to reduce creatinine
- When to see a Nephrologist
Creatinine Levels Chart (Age-Wise Normal Range)
| Age Group | Normal Creatinine Range (mg/dL) |
| Children (1–12 years) | 0.3 – 0.7 mg/dL |
| Teenagers (13–17 years) | 0.5 – 1.0 mg/dL |
| Adult Women | 0.5 – 1.1 mg/dL |
| Adult Men | 0.6 – 1.2 mg/dL |
| Adults above 60 years | 0.7 – 1.3 mg/dL |
Important: Slight variations happen due to muscle mass, physical activity, and lab methods.
What Creatinine Level Is Dangerous?
| Creatinine Level | Meaning |
| 1.2 – 1.8 mg/dL | Mild kidney stress |
| 1.8 – 3.0 mg/dL | Moderately high (possible CKD) |
| 3.0 – 5.0 mg/dL | Severe kidney damage |
| Above 5.0 mg/dL | Critical — dialysis may be required |
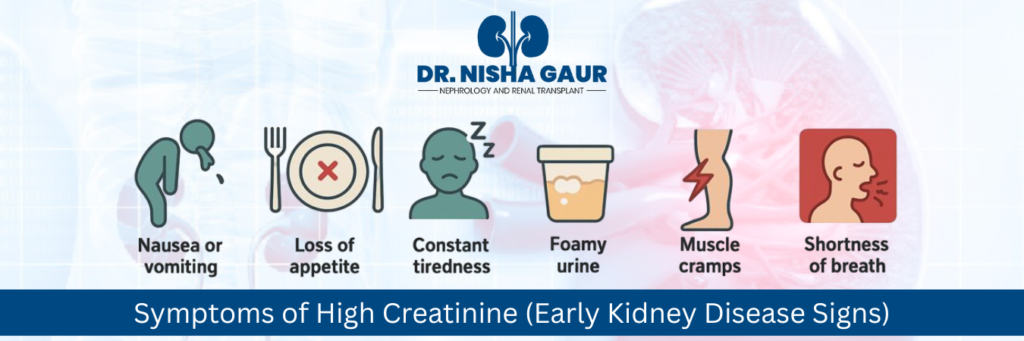
Symptoms of High Creatinine (Early Kidney Disease Signs)
If your creatinine is high, you may notice:
- Swelling in feet, ankles, or around eyes
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Constant tiredness
- Decreased urine output
- Foamy urine
- Muscle cramps
- Shortness of breath
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
Many people have no symptoms until their kidneys are already damaged, so regular tests are important.
Top Causes of High Creatinine
1. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
The most common cause — kidneys lose filtering power over time.
2. Dehydration
Low water intake can spike creatinine temporarily.
3. High-Protein Diet
Too much red meat, protein powder, or supplements.
4. Diabetes
Uncontrolled sugar damages kidney filters.
5. High Blood Pressure
Continuous pressure damages kidney blood vessels.
6. Painkillers (NSAIDs)
Ibuprofen, diclofenac and ketorolac can harm kidneys.
7. Urinary Tract Obstruction
Stones, prostate enlargement, or infection.
8. Certain Medicines
Antibiotics, steroids, and muscle-building supplements.

7 Fast Ways to Reduce High Creatinine (Scientifically Recommended)
1. Drink Adequate Water (But Not Excess)
Dehydration increases creatinine temporarily.
Aim for 2–2.5 liters/day unless your doctor advises otherwise.
2. Avoid High-Protein Foods
Temporarily reduce:
- Red meat
- Chicken
- Eggs
- Protein supplements
3. Lower Sodium Intake
Salt can worsen kidney filtration.
Avoid:
- Pickles
- Chips
- Processed foods
- Restaurant meals
4. Control Blood Pressure
Aim for BP below 130/80.
High BP is a silent kidney killer.
5. Manage Blood Sugar
Diabetes causes major kidney damage.
Maintain HbA1c < 7%.
6. Stop Painkillers
Avoid:
- Ibuprofen
- Diclofenac
- Ketorolac
These medicines directly damage the kidneys.
7. Add Kidney-Friendly Foods
Include:
- Lemon water
- Low-potassium fruits
- Barley water
- Garlic
- Cabbage
- Apple
- Cauliflower
These support filtration and hydration.

When to See a Nephrologist
Seek expert care if:
- Creatinine is above 1.8
- eGFR is below 60
- Frequent swelling or foamy urine
- Diabetes or BP for more than 5 years
- Kidney pain or repeated infections
Early treatment saves kidneys.
It may indicate moderate kidney damage—consult a nephrologist in Jaipur.
FAQs
You can reduce creatinine levels by reducing intense exercise, staying properly hydrated, and limiting red meat consumption. Focus on a low-protein, high-fiber diet featuring kidney-friendly fruits like apples and berries. Additionally, avoid supplements like creatine and consult your doctor about managing blood pressure or medications that may stress your kidneys.
Kidney failure (Stage 5 CKD) is generally indicated when your eGFR falls below 15 or your creatinine level stays above 5.0 mg/dL. At this stage, kidneys are functioning at less than 15% capacity. Because “normal” varies by age and muscle mass, doctors always use eGFR to confirm a diagnosis.
High creatinine levels are most commonly caused by kidney disease or impaired renal function, but they can also result from dehydration, high protein intake, or intense physical exercise. Other factors include certain medications, high blood pressure, diabetes, and the use of creatine supplements, which can temporarily increase waste levels in your blood.
Fruits that support kidney health and help lower creatinine include apples, blueberries, cranberries, and strawberries due to their high fiber and antioxidant content. Watermelon and pineapple are also excellent choices because they are low in potassium and help flush toxins. Always avoid high-potassium fruits like bananas and oranges if your levels are elevated.
Creatinine is a waste product that healthy kidneys filter from your blood. In kidney disease, the organs cannot remove it efficiently, causing levels to rise. Doctors use your creatinine level to calculate your eGFR (filtration rate); a high creatinine level typically indicates declining kidney function or advancing stages of chronic kidney disease.